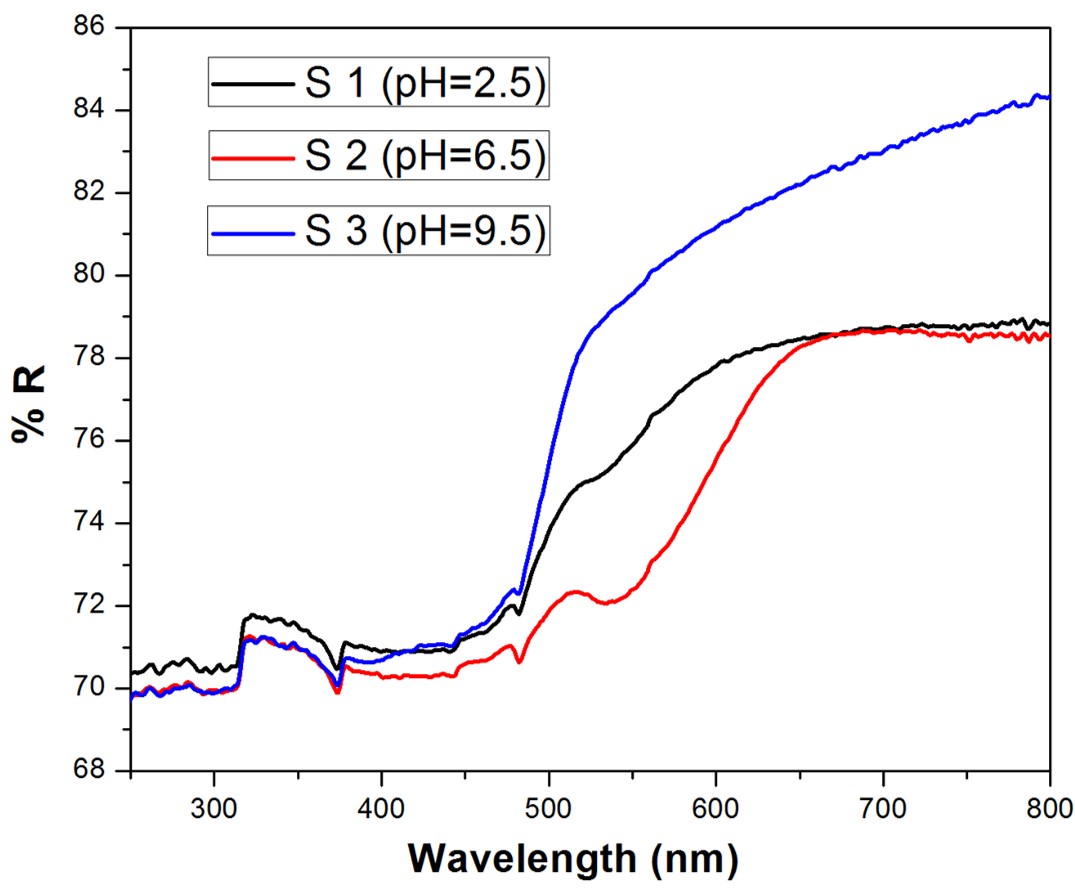
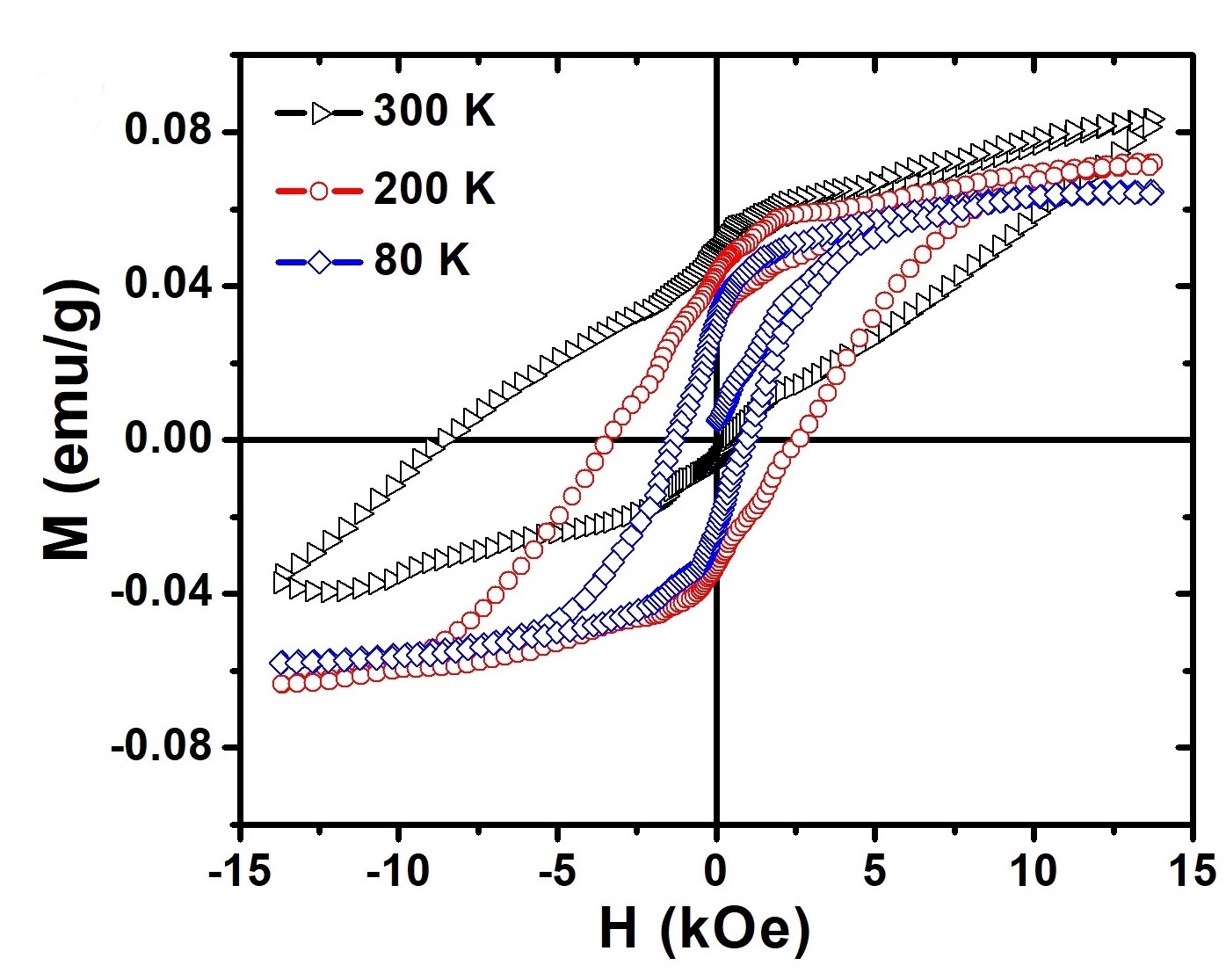
Role of Oxygen Vacancies in Oxide based Dilute Magnetic Semiconductor (CeO2 and TiO2)
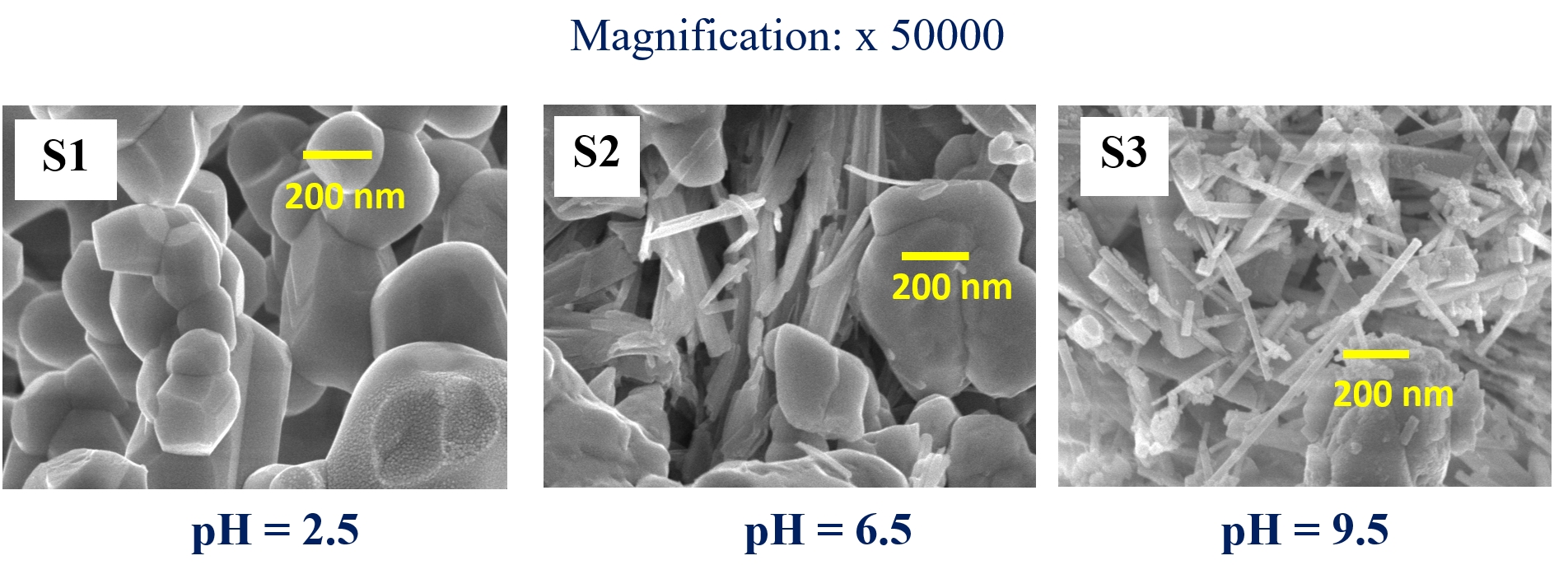
Ti(1-x)M(x)O2 and Ce(1-x)M(x)O2 nanoparticles (NPs) have been synthesized using sol – gel and hydrothermal chemical routes. Effect of heat treatment and doping of Transition and Rare Earth Metal ions on oxygen vacancy concentration in these nanomaterials have been investigated. Structural properties were investigated using XRD, Raman, HR – TEM and XPS analysis. Optical and Magnetic properties were investigated using UV – Vis and VSM analysis respectively. Photocatalytic dye degradation and hydrogen production by water splitting are currently under investigation.



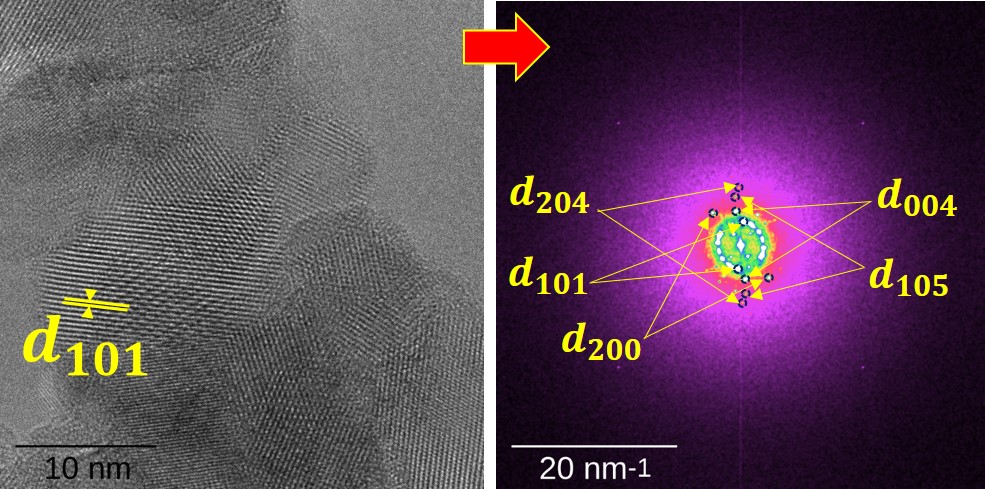
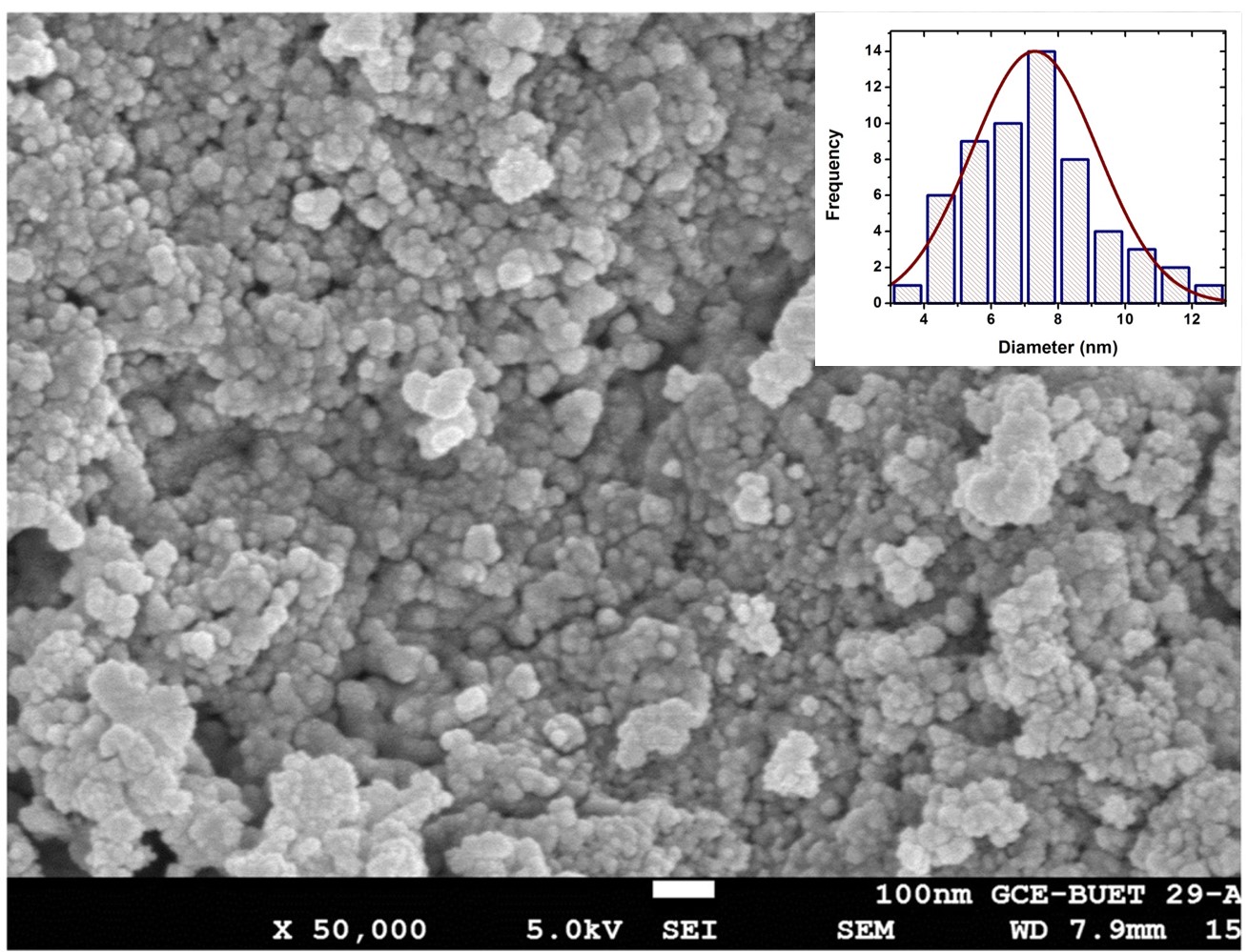
Structural & Property Correlation with Cytotoxicity & Antibacterial Activity of Green Synthesized Nanoscale Materials
This research focuses on green synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles (NPs) by using Ce(NO3)3.6H2O and aqueous leaf extract of Artocarpus heterophyllus as a bioreducing agent. The antibacterial activities of the NPs have been investigated against two gram positive (S. aureus and B. cereus) and two gram negative bacteria (E. coli and S. typhimurium) following disc diffusion assay. The cytotoxicity effect has been observed on two mammalian cell lines (HeLa and Vero). The structural characteristics of the NPs were revealed by X – Ray Diffraction, Raman, and FT – IR analysis while the morphology of the NPs was characterized by FESEM analysis.


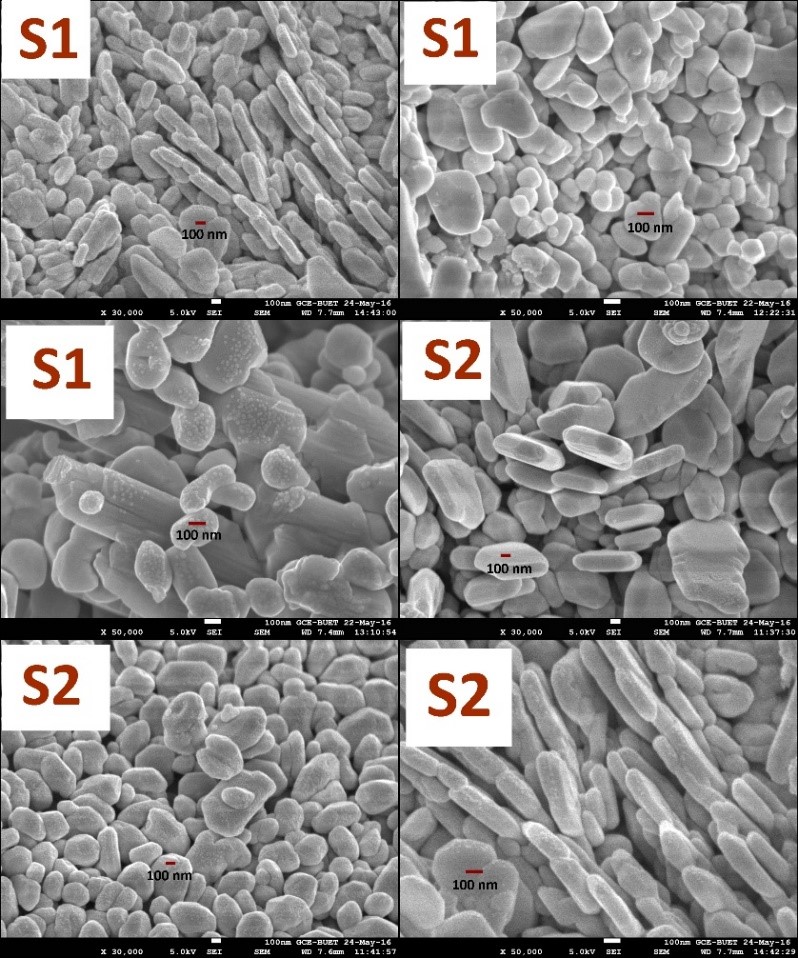
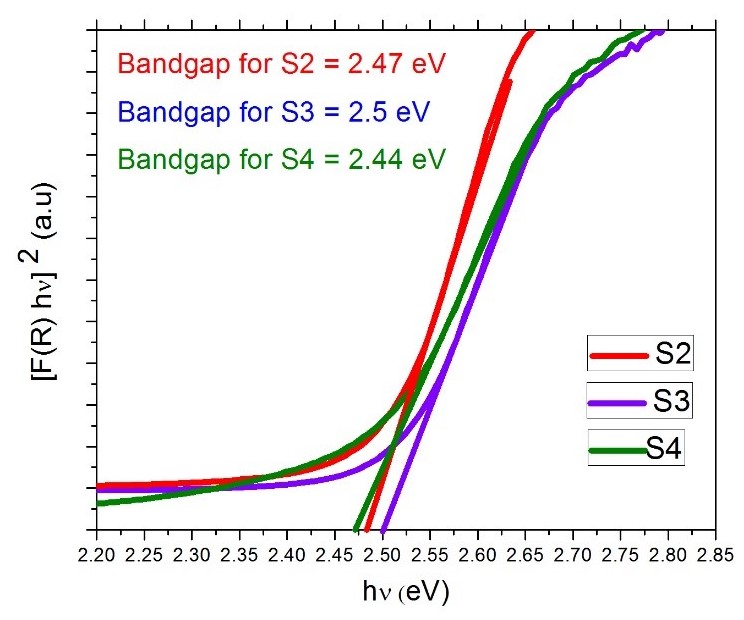
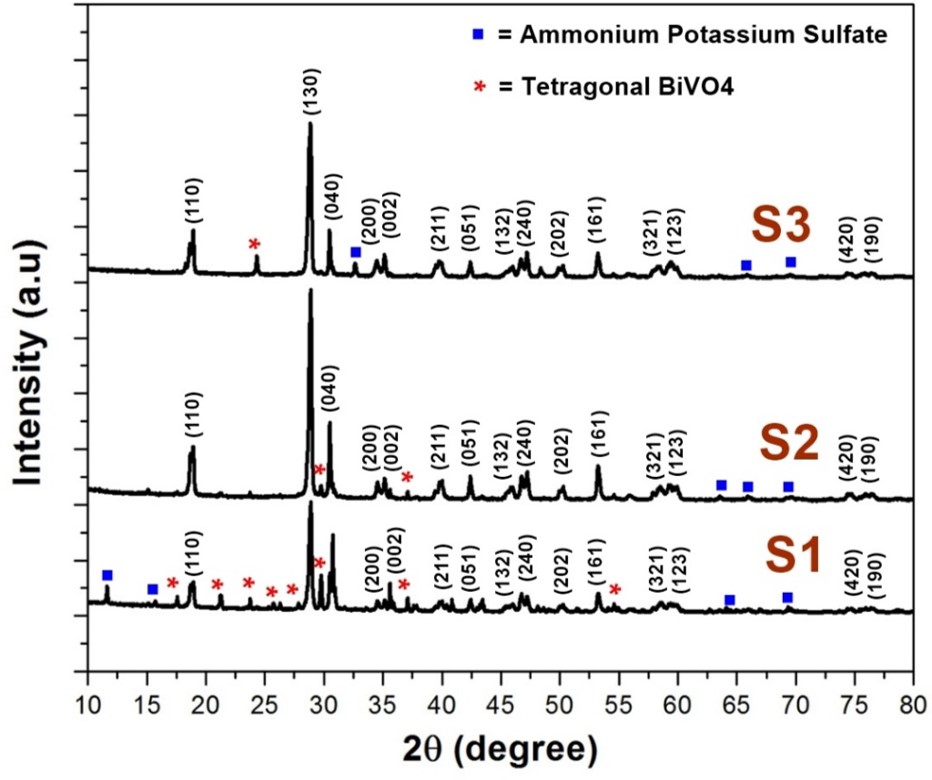
Investigation of lattice distortion in BiVO4
Pure monoclinic & doped BiVO4 were successfully synthesized by hydrothermal technique. We reported that 10% Nd doping at dodecahedral site has no effect on the lattice distortion but 10% Mn doping at tetrahedral site slightly distorted the lattice structure of BiVO4. From previous reports, it's well proved that monoclinic BiVO4 has lower bandgap due to the lattice distortion than tetragonal BiVO4. We recommended that variation in Mn doping percentage can be carried out to investigate the lattice distortion as well as lower bandgap of BiVO4.